Location -> News
News
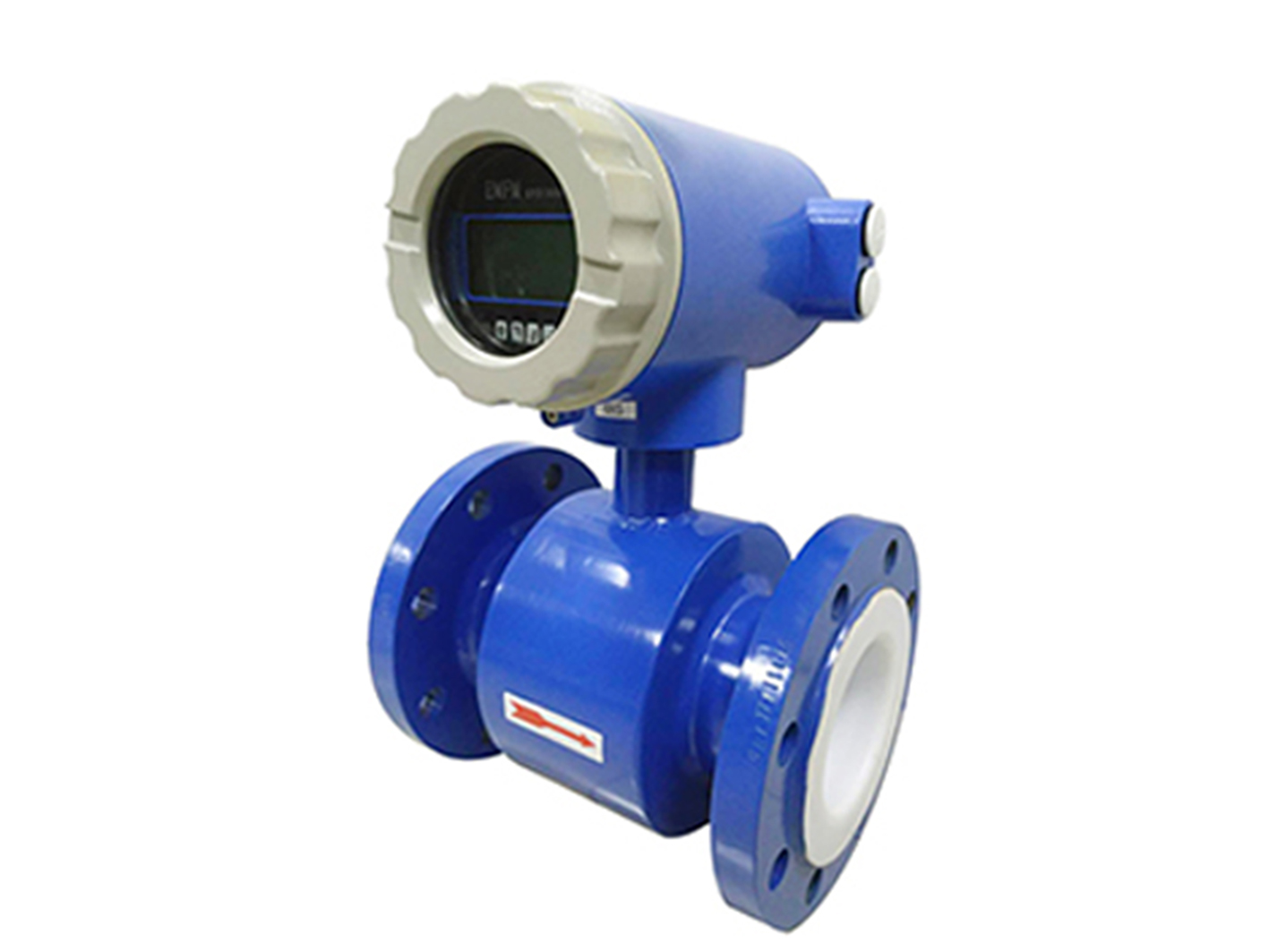
electromagnetic water flow meter working principle
Electromagnetic flow meter working principle
The operating principle of an electromagnetic flowmeter is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, which states that when a conductor moves in a magnetic field, an induced electromotive force (EMF) is generated that is proportional to the conductor's velocity and the strength of the magnetic field. The following is a detailed explanation of its working principle:
I. Basic Principle
Magnetic Field Generation: The sensor portion of the electromagnetic flowmeter is equipped with an excitation coil. When energized, it generates a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the pipe axis.
Electromotive force Induction: When a conductive liquid (such as water) flows through a magnetic field, charged particles in the liquid are deflected by the Lorentz force, accumulating charge on electrodes on both sides of the pipe, generating an induced electromotive force (voltage). The magnitude of this induced electromotive force is proportional to the liquid flow velocity and its direction is perpendicular to the magnetic field and flow direction (right-hand rule).
Flow Calculation: Flow rate is calculated using the formula
E=k⋅B⋅v⋅D
(or
Q=A⋅v
), where:
E
is the induced electromotive force.
k
is the meter constant.
B
is the magnetic induction intensity.
v
is the liquid flow velocity. D
is the pipe inner diameter.
Q
is the volume flow rate.
A
is the pipe cross-sectional area.
II. Signal Acquisition and Processing
Electrode Detection: Electrodes installed on both sides of the pipe inner wall directly contact the liquid to detect the induced electromotive force.
Signal Transmission: The electrodes transmit the weak electromotive force signal to the transmitter (converter).
Signal Processing: The transmitter amplifies, filters, and linearizes the signal to eliminate interference (such as power frequency noise and fluid electrochemical noise).
Output and Display: The transmitter converts the calculated result into a standard signal (such as 4-20mA, pulse, RS485, etc.) for display, recording, or control system use.
III. Structural Features and Advantages
No flow-blocking element: No moving parts in the pipe, minimal pressure loss, and long service life.
Anti-interference design: Low-frequency rectangular wave excitation is used to reduce power frequency interference; the electrodes are flush with the lining to prevent sediment accumulation.
High Precision and Stability: Measurement accuracy can reach ±0.5%, with minimal impact on fluid density, viscosity, temperature, and pressure. Wide range ratio: With a range ratio of up to 100:1, it's suitable for measuring low to high flow rates.
High adaptability: It can measure corrosive liquids and liquids containing solid particles (such as sewage and slurries), but requires a liquid conductivity of 5μS/cm or higher.
For more information on electromagnetic flowmeter selection and pricing, please contact us by email:
sales01@cxflowmeter.com
sales01@cxflowmeter.com
WhatsApp: 008618049841995
Last:沒有了 Next:Core Analysis of Drain Pumps wi..